By Amir Delgoshaie, Senior Director, Data Science, Ishaan Gupta, Senior Software Engineer, Akshay Punhani, Manager, Data Science, Nikhar Maheshwari, Data Scientist, Harsha Vaddi, Data Scientist, Nishanth Mohankumar, Data Scientist, Dylan Ferris, Lead Software Engineer
Coding agents have dramatically accelerated application development. What they have not reliably delivered — until recently — is enterprise-ready software. Production systems demand more than speed: they require security, governance, durability, and consistency across runs and deployments.
Agentic AI has now matured to reliably translate natural-language prompts into enterprise-ready applications — when paired with the right foundation. C3 AI’s agentic development stack provides that foundation, enabling teams to build secure, reliable, and fully deployable applications in hours instead of weeks.
By combining specialized coding agents with proven enterprise application infrastructure, C3 AI allows developers of all levels to move faster while meeting the operational, security, and governance standards enterprises expect.
There are three core components in the C3 AI agentic development stack that make this possible:
- High-value application templates and instruction sets that encode best practices and ensure consistency.
- A domain-expert LLM trained for enterprise software and C3 AI applications, capable of generating production-quality code for core application components.
- The C3 AI Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server, which connects coding agents to C3 AI–specific tools, prompts, and validation workflows
Together, these components allow users to go from prompt to production at speed and at scale.
The Promise and Pitfalls of Coding Agents
Coding agents are transforming how software is built. Development is faster, more automated, and more accessible — for not only developers, but for everyone. Non-technical teams can now build, customize, and extend applications independently, while AI-powered tools handle tasks that once required deep, specialized expertise.
Benchmarks such as SWE-bench and SWE-Bench Pro illustrate how far these tools have advanced. Modern coding agents can resolve bugs and implement enhancements across large open-source and commercial projects, demonstrating real value well beyond demos or prototypes.
Developer-focused tools like Claude Code, Codex, GitHub Copilot, and Cursor have become integral to many engineering workflows, significantly improving productivity and speed. At the same time, visual and agentic design tools such as Bolt, Lovable, and V0, have emerged as intuitive platforms that allow users without formal coding experience to build sophisticated applications. Together, these tools point toward a future where agentic development becomes the default mode to software creation.
Yet despite this progress, building production-ready Enterprise AI applications with coding agents alone remains challenging. While these tools excel at prototyping, the resulting applications often fall short of enterprise requirements for rigor, reliability, and maintainability.
Consider a manufacturing engineer building an asset-monitoring solution. A coding agent can quickly generate a clickable UI and basic workflow logic to monitor data output and assess the health of industrial assets. But a production-grade application requires much more: a robust data model, reliable data ingestion pipelines, fine-grained user and role management, machine-learning (ML) model lifecycle management, deployment and observability workflows, and strict data access controls.
Generating these components from scratch for every application is inefficient — and unreliable. Coding agents are inherently non-deterministic, meaning the same prompt can produce different results across different builds. As a result, critical enterprise features cannot be consistently reproduced.
Where coding agents excel is in assembly. When provided with proven, enterprise-ready app components such as data ingestion pipelines, user role management, and data access controls, agents can focus on writing the connective “glue code” that ties everything together. This approach dramatically accelerates development while preserving the accuracy and durability that enterprises demand.
Fusing Coding Agents with Enterprise Expertise
The C3 Agentic AI Platform is built to support the assembly of agentic AI software. It provides data models, pipelines, access controls, deployment workflows, model management, and the other required building blocks for enterprise-ready AI applications.
At the heart of this platform are three core components that enable rapid, reliable, and enterprise-grade development:
- Application templates and instruction sets for high-value use cases
Ready-to-use templates and instructions help build applications from scratch or configure and extend pre-built C3 AI solutions. These templates enforce development best practices, ensure consistency, and dramatically reduce development time. They also improve efficiency by reusing components rather than generating them from scratch, lowering token usage and reducing the variability associated with non-deterministic LLM outputs. Templates make application generation faster, cheaper, and far more repeatable. - A domain-expert LLM trained for enterprise software and the C3 AI stack
Our in-house LLM is built to understand enterprise application requirements and generate production-quality code for all C3 AI app building blocks. This model is trained on our rich code bases and is fine-tuned to be an expert in writing C3 AI application code. - An MCP server that connects external coding agents to specialized C3 AI tools
Through our MCP integration, leading coding agents can call into our domain-specific LLM, specialized tools, and task-optimized prompts directly from the developer’s IDE. This creates a seamless workflow where general-purpose agents handle routine development tasks and our platform-specific LLM and tools manage domain-critical components requiring enterprise-grade precision and structure.
This architecture has been proven in production by large enterprises and allows teams to combine the speed of coding agents with enterprise-grade rigor.
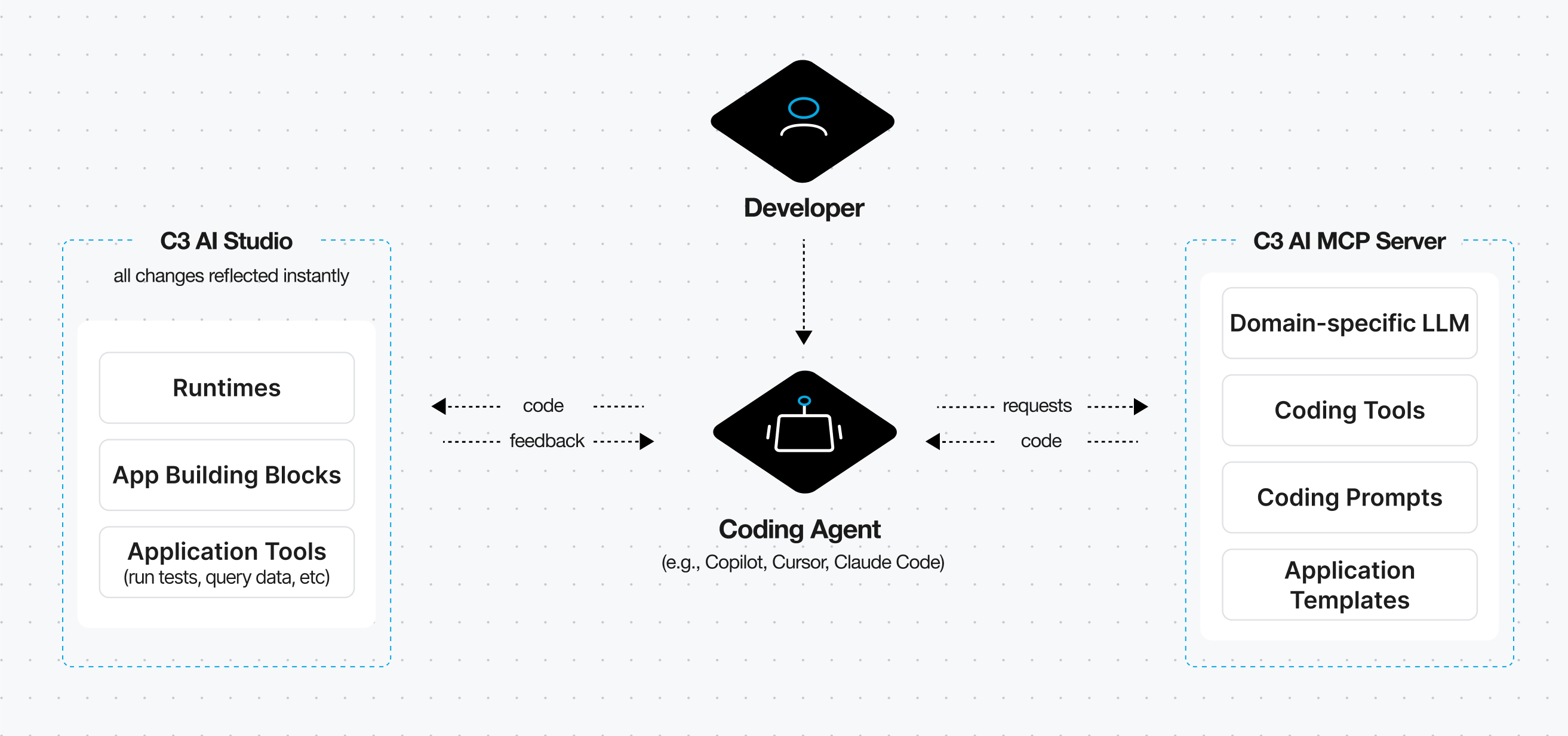
Figure 1: Architecture of the C3 AI agentic development stack. A developer interacts with a coding agent directly from their IDE. The coding agent communicates with the C3 AI MCP Server to access domain-specific LLM capabilities, coding tools, prompts, and application templates. It then generates and updates application code, syncing changes with C3 AI Studio, where updates are reflected instantly. As the agent iterates, it receives feedback from C3 AI Studio to refine and validate its work. Users can see their application evolve in real time as they collaborate with the coding agent.
The C3 AI Agentic Development Stack in Practice: Building an Asset Management Application
To illustrate how this works end-to-end, consider the development of an asset monitoring application.
Starting from a blank workspace, a developer describes application requirements in natural language. As the coding agent works, new components appear immediately in C3 AI Studio — data models, APIs, and UI elements — ready for inspection and iteration.
Each step builds on the same foundation:
- Templates establish structure
- The domain-expert LLM generates production-quality components
- MCP connects the agent to platform-specific capabilities
As the application evolves, the developer:
- Iterates on the UI conversationally
- Connects production data sources through no-code configuration
- Adds complex backend APIs
- Generates and executes unit tests
- Defines fine-grained access roles
- Enables JupyterLab for analytics and ML development
Multiple teams can work in parallel, all against the same governed application foundation. Let’s dive into the details.
Step 1: Kick-Starting Development
For the purposes of this demo, we’re using VSCode with Github Copilot, though the same flow will work with any coding agent. We begin in an empty directory in VSCode, connected to the C3 AI MCP Server and a C3 AI development environment. With a simple prompt, the developer asks the coding agent to build a data model, basic API logic, and a first version of the UI.
As shown above, GitHub Copilot uses the C3 AI application template to create a new application with the correct folder structure and scaffolding. The agent outlines a multi-step development plan: creating the data model, adding sample data, generating backend logic, and drafting the initial UI.
Because the development environment is connected to C3 AI Studio, the application immediately appears there, where the user can explore the generated UI and inspect the newly created data model.
Step 2: Iterating on the UI and Data Sources
Next, the developer refines the application through conversational updates: asking the agent to modify the UI and expand sample data. The changes are executed automatically.
As seen in the video above, changes made via natural language prompts are instantly reflected in the application UI within C3 AI Studio. These interactions enable a fluid, interactive development loop.
Step 3: Connecting to Production Data
The application is then configured to use production data sources, instead of the original sample data.
Using the no-code capabilities of C3 AI Studio, the user configures Snowflake as a data source. The agent then updates the application configuration to link the new data source directly to the data model, no manual wiring required by the developer.
Step 4: Adding Complex Backend APIs
The agent is also capable of generating sophisticated logic to integrate complex backend APIs. In this asset monitoring example, the developer adds an API to summarize event statistics by location.
The new API appears automatically within the application’s data model in C3 AI Studio, ready for immediate use by the UI to pull in and display the requested metrics.
Step 5: Validation and Bug Detection
By this stage, the application contains substantial logic that must be validated through testing. A single prompt instructs the agent to generate unit tests for all methods on the event entity and run them until they pass.
Because the agent is connected to our development environment, it can execute these tests and iterate until the entire testing suite passes, providing an additional layer of accuracy and trust in the generated code.
Step 6: Defining and Managing Custom Access Roles
Due to tailored permissions for the many different types of users within enterprise applications, the systems require fine-grained access controls. In this app configuration example, the developer adds a custom role for plant managers, enabling role-specific permissions to add and remove assets from the application.
Guided by a simple prompt, the agent defines the boundaries of the new role and assigns user-level permissions. This quickly sets up consistent role-based access controls across the application.
Step 7: Enabling JupyterLab for Data Science and Machine Learning
Once the first version of the application is ready, data scientists can immediately explore the application through JupyterLab, a fully connected development and analytics service available within C3 AI Studio.
JupyterLab has full access to the same data model, application data, and APIs created by the coding agent, allowing data scientists to run analytics, build ML models, and validate results directly on top of the application. Different teams can work on the same application in parallel, with engineers adding UI and backend features, and data scientists building the analytics and modeling capabilities.
What’s Next
The asset monitoring example illustrates what’s possible when powerful coding agents are paired with a proven enterprise foundation: sophisticated, production-grade applications can be built and deployed with speed and reliability. And this is only the beginning.
As coding agents continue to evolve — and C3 AI expands its tools, templates, and development patterns — the C3 Agentic AI Platform will keep extending what teams can build with and for Enterprise AI, from initial prototype through full production deployment.
Ready to try these agentic workflows yourself? Join the next C3 Generative AI Accelerator — a series of live workshops that will teach you how to move prompt to production.
We’re excited to see what you build — share your work by tagging us on LinkedIn and X.
About the Authors
Amir Delgoshaie is a Senior Director of Data Science at C3 AI, where he leads generative AI foundations for developer productivity, including domain-specific LLMs, MCP infrastructure, and coding agents used to build enterprise applications. He previously worked on core components of the C3 Agentic AI Platform and led the development and deployment of large-scale AI applications across energy, utilities, manufacturing, and supply chain.
Ishaan Gupta is a Senior Software Engineer at C3 AI, specializing in large-scale LLM systems, developer tooling, and Enterprise AI workflows. He leads the development of agentic platforms, evaluation frameworks, and next-generation MCP infrastructure, improving engineering productivity and accelerating AI adoption across the organization. Before joining C3 AI, he was a Software Engineer at Meta, where he worked on large-scale recommendation systems. Ishaan holds dual bachelor’s degrees in computer science and electrical & computer engineering from Carnegie Mellon University.
Nikhar Maheshwari is a Data Scientist at C3 AI, focused on advancing generative AI capabilities and developer productivity across the C3 AI Platform. His work spans large-scale data curation, synthetic data generation, LLM fine-tuning, and evaluation frameworks that power the C3 AI Code Assistant and related LLM initiatives. He previously worked at Samsung Research on deep learning models optimized for low-resource edge devices. Nikhar holds a master’s in computer science from Stony Brook University.
Harsha Vaddi is a Data Scientist at C3 AI, focused on Applied AI and LLM research. He develops scalable AI capabilities across developer-facing platforms, improving model quality and user experience through advancements in retrieval, evaluation workflows, and intelligent assistant systems. His work spans data engineering, model development, and automated evaluation, and he works extensively with reinforcement learning and large-scale LLM techniques to solve real-world enterprise problems. Harsha holds a Master of Science from the Georgia Institute of Technology and a bachelor’s degree from the Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad
Nishanth Mohankumar is a Data Scientist at C3 AI, where he builds generative AI capabilities that enhance the C3 AI development experience. Among other things, his work centers on iterative improvement driven by user feedback, developing large-scale synthetic data generation pipelines for LLM training and evaluation, etc. Nishanth holds a master’s degree from Carnegie Mellon University and a bachelor’s degree from National Institute of Technology, Karnataka.
Akshay Punhani is a Data Science Manager at C3 AI, where he focuses on enhancing developer productivity across the C3 Agentic AI Platform by building tools that streamline development, testing, and deployment for engineering and data science teams. He has also contributed to major initiatives in Sustainability, Asset Performance, and Generative AI, supporting both customer engagements and product development. Akshay holds a master’s in data science from the University of California, Berkeley.
Dylan Ferris is a Lead Software Engineer at C3 AI, where he builds enterprise applications, developer tools, and product prototypes used across the organization. He has led full-stack development efforts, created internal tooling to streamline engineering workflows, and contributed to product demos and innovation initiatives. He focuses on delivering reliable, user-centric software that supports teams and showcases the capabilities of the C3 Agentic AI Platform.



